The Birth of Sunspots and Black Hole Collisions
How are sunspots born? What does a black hole collision look like? How long does it take to make a full-size galaxy? This month on Naked Astronomy, we find out why people searching for pulsars might spot colliding black holes in their data, how galaxies may form quicker than predicted, and where in the sun sunspots first arise. Plus, news from gravity probe B, why there's no more space on the moon for craters, and how as many as half of all hot Jupiters may be spinning the wrong way.
In this episode
01:21 - Results from Gravity Probe B
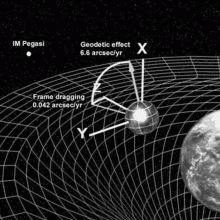
Results from Gravity Probe B
Results from Gravity Probe B test and support Einstein's theories of relativity - and have only been 50 years in the making! The results confirm that massive objects really do warp spacetime, even dragging it along as they spin...

04:17 - Orbiting the Wrong Way
Orbiting the Wrong Way
Up to half of all hot Jupiters may orbit their parent star contrary to the star's direction of rotation. New models suggest that they may be flipped by interaction with another body in the solar system...

08:36 - Topology of the Moon
Topology of the Moon
Data from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) on NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter has given us a unique insight into the "roughness" of the moon's surface, telling a story of meteor bombardment throughout lunar history...

11:36 - Molecular Gas from Galaxies
Molecular Gas from Galaxies
Molecular gas streaming away from galaxies has been spotted by the Herschel Telescope. This gas could be responsible for limiting galactic growth, and streams out at such speed that it raises important questions about where its energy comes from...

14:23 - Io's Magma Middle
Io's Magma Middle
Jupiter's moon Io is known to be highly volcanically active - now, data collected by the Gallileo craft looking at the interaction between Io and Jupiter's magnetic fields suggests that there's a global magma ocean in Io's interior...

24:23 - Fact Impact - Mars
Fact Impact - Mars
with Dominic Ford, Cambridge University

- Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System.
- It lies just outside the orbit of the Earth.
- In the night sky it appears red, a similar colour to a rusty nail...
- ... in fact, a very similar colour; a major constituent of Martian soil is iron oxide, which is better known as rust.
- It's the second smallest planet in the Solar System, half the size of the Earth.
- And yet it plays host to the largest mountain in the Solar System, a volcano known as Olympus Mons, which is three times higher than Mount Everest here on Earth.
- Its atmospheric pressure is less than a 100th of that on Earth.
- On the Earth that's equivalent to the pressure at an altitude of 100,000 feet.
- At such low pressure, liquid water would evaporate almost immediately.
- So while there's plenty of water on Mars, it's all locked up in ice reservoirs beneath the surface.
- And what little air there is on Mars is mostly carbon dioxide, with barely a trace of breathable oxygen.
- At the poles, this gets so cold that it forms frost. Not made of ice, but made of solid carbon dioxide at -120 C.
- So, the surface of Mars is a harsh place. Moreover, with no magnetic field to deflect it, Mars' surface receives the full brunt of the ionising radiation emitted by the Sun.
 But it might not always have been that way. The surface of Mars shows signs of past water erosion.
But it might not always have been that way. The surface of Mars shows signs of past water erosion.- So, it probably had a thicker atmosphere and a warmer climate in the past.
- And may well have been much more habitable back then.
- Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, named after the sons of Mars in Greek mythology.
- But they're much smaller moons than our own, measuring less than 25 km across.
- They orbit so close to Mars that they're difficult to spot, even with a sizeable telescope.
- And it's quite a mystery where they came from. They may well once have been asteroids that slipped into orbit around Mars.
- More spacecraft have been sent to study Mars than any other planet.
- The success rate has been low; of 33 missions launched; only 15 have returned useful data.
- ... but the latest rovers to land on the Martian surface, Spirit and Opportunity, have lasted over six years, well beyond their 90-day design lifetime.
 |  |  |
 |  |  |

How fast do Galaxies Grow?
with Claire Burke, Liverpool John Moores University










Comments
Add a comment