Ingredients
 | Polarising or polaroid sunglasses (often used for driving, fishing or sailing) |  | A modern flat computer screen or LCD TV |
Instructions
Hold the sunglasses in front of you and then rotate them. Do you notice anything odd?
Try filling a sink with water. Move your head so that you can see something bright reflected in the water. Put the sunglasses in front of the reflection and then rotate them.
You can also try making an area of your monitor white, look at some transparent polythene in front of the monitor through your glasses. Now stretch the polythene and look at it in front of the monitor through the glasses. Try rotating the glasses.
Result
If you have the correct type of sunglasses you should find that the image from the computer screen appears and disappears as you rotate the sunglasses.
If you look at a reflection in water and rotate the sunglasses it should appear and disappear depending on the angle of the glasses.
Stretching Plastic
If you put plastic between the screen and the glasses it will look quite boring but if you stretch it you should see wonderful colours. If you rotate the glasses the colours will change.
| |
Explanation
This experiment works because light is a transverse wave. This means that the vibration is at right-angles to the direction of travel so the light can vibrate in different directions while travelling in the same direction This direction of vibration is called polarisation.
The sunglasses are made of a material which will only let vertically polarised light through and not the horizontally polarised light. Materials which can do this are called polarisers.

If you have two pieces of polariser which are aligned in the same direction they will both let vertically polarised light through. However, if they are crossed then the first will only let one polarisation through but the second piece will only let the other through, so no light will go through.
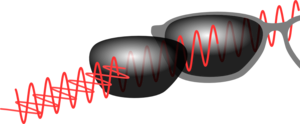 | 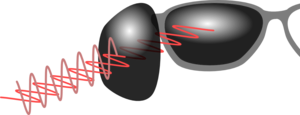 |
| If the two polarisers are aligned light will go straight through. | If the polarisers are aligned in different directions then one polariser will stop one polarisation and the second the other, so no light will get through. |
Why are sunglasses made of polariser?
Sunglasses used by fishermen, sailors and often drivers are polarising because light reflected from water is mostly horizontally polarised. By using a vertical polariser you can cut out most of these reflections and glare.
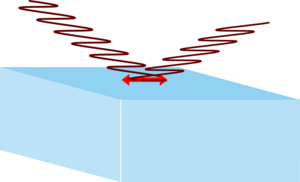 | 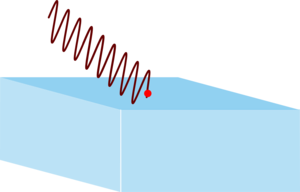 |
| Horizontally polarised light hitting a water surface will move electrons in the surface in such a way as to reflect the light. | However vertically polarised light will try to move electrons vertically, which would mean moving them out of the surface which is not possible. The light isn't reflected. |
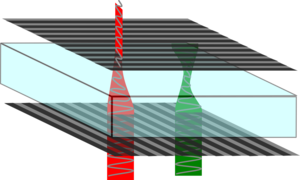
Why can you see through crossed polars with stretched plastic in between?
The plastic will rotate the polarisation of light so some of it will now get through the polarisers. It will rotate some colours of light more than others so the light which can get through the second polariser will be coloured. As you rotate the polariser you will let colours with different polarisations through and because different colours now have different polarisations you will see different hues.
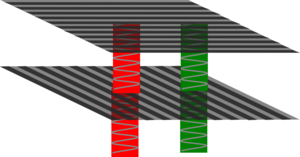 |  |
| If you have crossed polarisers no light can get through. | However stretched plastic will rotate different colours of light different amounts so the light which gets through the second polariser will be coloured. |
How does a polariser work?
Light is an electromagnetic wave and the vibration is actually an electric field and so if light hits a conductor it will create a vibrating electric current in the conductor.
The polariser is made up of lots of long thin molecules which conduct electricity. When light hits the polariser which is polarised in the same direction as the molecules it will cause electric currents to flow through along the molecules. This takes energy out of the light wave and stops it. However if the light wave is polarised in the other direction no currents can flow so the light carries straight on.
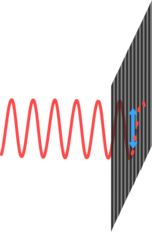 | 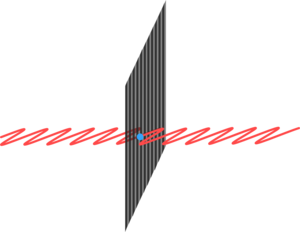 |
| One polarisation of light will move electrons along the conducting molecules absorbing energy from the light. | The other polarisation can't drive electric currents as there are no molecules pointing in this direction so the light is not absorbed. |
Why does the computer screen produce polarised light?
A flat screen computer monitor is also known as a liquid crystal display (LCD). The liquid crystal is trapped between two layers of glass and is made up of long thin stiff molecules. These tend to line up with one another. The two pieces of glass are scratched which tends to align the molecules with the scratches.
The scratches are aligned in different directions on the two pieces of glass, So a twist in the liquid crystal develops which will rotate the polarisation of light. So if you put it between crossed polarisers the light can now get through.
If, however, you apply an electric field the molecules align in a position perpendicular to the pieces of glass and stop twisting the light. The light can't get through so the area looks black.
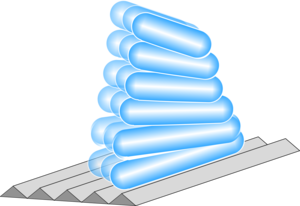 | 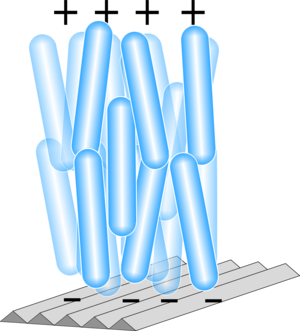 |
This is how watch displays work. Here is a simple LCD display first without a second polariser and then with one.
A computer monitor works the same way but has millions of pixels: each with a different coloured filter in front of it so it can make up different colours. The light leaving it has been through a polariser and is polarised.
- Previous Liquid Nitrogen Bomb
- Next The Gherkinator










Comments
Add a comment