How do Vampires Go for the Jugular?
We'll find out how vampire bats home in on hot blood in this week's NewsFlash! Also, we explore the idea that Earth once had two moons, find out how researchers are making functioning brain cells from adult skin cells, and celebrate the first men to visit Jupiter, as NASA launches the Juno mission with its crew of three Lego men...
In this episode

00:30 - Earth's Multiple Moons
Earth's Multiple Moons
A paper published in this week's issue of the journal Nature presents evidence that the Earth might once have had a second moon, based on a puzzling problem with the geology of the Moon's surface. Even to the naked eye, it's possible to differentiate the Moon's surface into dark flat volcanic planes, the seas, and much lighter coloured rougher mountainous regions, the highlands. The visible shape of the boundary between these regions is what some have romantically called "The Man in the Moon".
What's puzzling is that on a body as large as the Moon, you'd expect the flat planes and the mountainous highlands to be randomly distributed over its surface. In fact, the seas are tightly clustered together on one side of the Moon, whilst the other side is much rougher. Such a large inhomogeneity seems beyond what could be expected from random processes alone.
 In this week's issue of Nature, this puzzle has led Martin Jutzi and his colleagues at the University of California reconsider the traditional view of how the Moon formed. The standard view is that around 4.5-billion years ago, a planet around the size of Mars, sometimes called Theia, collided with the Earth. Both planets were entirely melted by the energy of the impact, and a small globule of this molten rock separated from the rest to become the Moon.
In this week's issue of Nature, this puzzle has led Martin Jutzi and his colleagues at the University of California reconsider the traditional view of how the Moon formed. The standard view is that around 4.5-billion years ago, a planet around the size of Mars, sometimes called Theia, collided with the Earth. Both planets were entirely melted by the energy of the impact, and a small globule of this molten rock separated from the rest to become the Moon.
Jutzi considers what would have happened if, instead of a single moon forming out of this collision, in fact two moons had been formed. His conclusion is that two moons could have co-existed in orbit around the Earth for around a hundred million years, but they would eventually have collided. Could such a collision have led to the lop-sided shape of the Moon that we see today?
One obvious problem with that idea is described rather well by Jutzi in his paper: when astronomical bodies collide, the result is usually to make holes in things -- craters and basins. In this case, something made mountains on one side of the Moon. So, Jutzi sets out to investigate whether a collision could ever deposit mountains onto the surface of a body. And he argues that if the relative speed of the two bodies is small enough, there isn't enough energy to excavate a large crater, and instead the result is a large pile of rubble rather resembling mountains.
An interesting further outcome of Jutzi's computational models is that, in this scenario, the molten magma in the interior of the Moon is pushed towards the Moon's opposite hemisphere by the force of the impact, which might in turn lead to increased volcanism around the point on the Moon opposite to the point of impact, and so the formation of volcanic planes, as we in fact see.

05:40 - Lego men going to Jupiter
Lego men going to Jupiter
NASA's most recent mission to Jupiter called Juno was launched this week with a crew of three. The three aren't normal astronauts however, they are 3 Lego figures attached onto the spacecraft.
The figures are representations of the roman god Jupiter, his wife Juno, and Gallileo who was the first person to discover moons around jupiter, and for that matter around any other planet.
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system, and contains more mass than all the other planets combined, and so probably started forming before the other planets. Juno is going to study the atmosphere and magnetosphere of Jupiter to try and discover more about its composition and structure.
The figures should be going on a long journey of about 2.8 billion km, first on an orbit that sends them just outside Mars, then getting an additional kick from earth's gravity in 2013, and arriving at Jupiter in 2016, when Juno can start its mission.
Unfortunately for any Jovian children who may come across these lego men, they are made out of solid chunks of aluminium, and aren't articulated, so playing with them might be rather dull. This is probably because the plastics used to make normal lego-men haven't been approved for use on space missions and might emit substances which could fog up a lens, or interfere with an instrument, but the idea is to inspire children on earth by taking something they associate with on an amazing journey.

08:45 - Homing In With Heat - Vampire Bats find Blood
Homing In With Heat - Vampire Bats find Blood
Professor David Julius, University of California, San Francisco
Chris - How do blood thirsty vampire bats home in on the best place to bite and therefore guarantee achieving a trouble-free feed? Well the answer is that they've evolved their own built-in infrared detectors to pinpoint where the best blood vessels are and David Julius from the University of California San Francisco is behind the discovery. Hello, David.
David - Hello.
Chris - What made you think that bats might actually be resorting to temperature to guide them to where they should sink their teeth in this way?
David - So, it's been known for several decades that bats have these so-called pit organs on their face that are heavily innervated with nerve fibres that allow them to detect infrared radiation. What we've done is to ask what the molecular underpinnings of that system might be.
Chris - So how these special pit structures on their faces can actually pick up infrared or heat?
David - That's right.
Chris - How did you approach it? What did you do?
David - We're more generally interested in the whole mechanism of temperature sensation, how we, as humans for example detect things like hot and cold, and we've been interested in finding out how this works in animals that really take thermal sensation to the extreme in a way and use this in a different but generally related manner. And what we did was use some new methods in genomics, what they call deep sequencing or DNA sequencing where we can profile all the genes that are expressed in different tissues, and we ask what kind of molecules are expressed in the nerve cells that send their projections to these heat-sensing pits, and are known to be involved in the infrared detection mechanism. And we look through those to find molecules that might be involved in this form of what turns out to really be heat sensation.
Chris - Okay, so we know that our skin is sensitive to heat and we have a pretty good idea how it detects heat. There are various chemicals which are on the surface of nerve cells that sensitise those nerve cells when the temperature goes up. So, are you saying that a variant of one of those is being used by the bats on their face in order to not just detect temperature but to specifically detect temperature relevant to body heat?
David - Yes, that's exactly the case. So, what we've shown is that the bat expresses a form of a protein that we also use to detect heat. But the form of the protein that the bat expresses is in some ways optimised where the temperature required for activation is lower than it is for our heat sensors and enables them to detect body heat coming from their prey, from a blood supply from a cow or a pig, what have you. So the basic underlying mechanism is the same as the one we use, but they have some little bit of genetic trickery that enables them to modify the protein so that it's more sensitive to heat and can pick up radiant heat from their blood supply.
Chris - So they're using the same genetic machinery that they would use elsewhere in the body to pick up when they're being burned or things are getting too hot. But in these special facial regions, they are tweaking the gene a bit so that it becomes more sensitive at a lower temperature so they can use those organs to see where there is heat radiating from the right bit of an animal they want to bite, so they can infer where the blood vessels must be.
David - Right, exactly. In a body of a mammal, the sensory nerve fibres for example that allow you to sense temperature, touch or pain are distributed into different - what we call ganglia - that contain clusters of nerve cells. And those that innervate everything from the neck down are in one set of ganglia and those that innervate everything from the neck up are in another set. And in our bodies those two sets of neurons are more or less the same. There are some slight differences in the expression of genes, but pretty much what you see in one cluster of neurons is the same as in the others. And in the vampire bat, what we found is that in this particular gene that expresses this heat sensor, the nerve clusters that send nerve fibres to everything from the neck, up to the facial area, which includes the heat-sensing pits, the expression of the heat sensors are different, and the protein coming from gene is modified so that it takes on this different form. And in fact, that's one of the big clues that tells us that this gene is likely involved in this specialised function of the vampire bat, namely infrared sensation, because it is modified and it's modified only in those clusters of nerve cells that send their nerve fibres to this region of the body that is involved in infrared detection.
Chris - There are other animals that also home in on heat. There are some snakes and vipers for example that aim for the hot spot because that's where they want to invenomate because they, I guess, figure that if they put the venom where the heat is, that's where the blood is so it will act most quickly, and then also guarantee a strike on the animal. Do they use the same mechanism as your bats then?
David - They use a mechanism that's related but in detail, different. One of the great example of this in terms of pit vipers is the snake that lives out around my area here called the Western Diamond Back Rattlesnake, and it also has what we call "facial pits." They're somewhat different in structure that a vampire bat but generally have a similar plan and they detect radiant heat say, from a squirrel or a mouse that they're trying to find in a dark burrow at night, so it allows them to see the animal as a radiant illuminated figure. They use a protein molecule that detects temperature that's a member of the same protein or gene family as the one found in the vampire bat, and the one that we use for heat detection. It's encoded by a different gene, but they're part of the same gene family. And so overall, the mechanism is similar but the exact molecule that's used is different in its detail and in its structure.
Chris - And just to finish up, David. Given that you've got this new insight into how this gene can change its behaviour if you do what the vampire bats are doing to it, in other words, make it sensitive at a lower temperature. How does this inform our understanding of how pain is signalled in the nervous system and could there therefore be some uses of what you've discovered?
David - Yeah, so that's an excellent question, and a molecule that we express, which by the way I should say is the target for things like chilli peppers. So, the molecule that we're talking about here that's involved in temperature sensation in the bats and in our own nervous system is what allows us to appreciate sort of that hot zing from chilli peppers. We're interested in that molecule, as are many other labs, because there's evidence to suggest that its also modified by agents that are produced during inflammation and tissue injury that then sensitise the whole system so that you now for example would appreciate a lower temperature as being sometimes painful. So the example would be, if you have a sun burn and then you get in the shower and the temperature is normally what you'd consider to be warm and very comfortable, you might consider that or perceive that as being noxiously or painfully hot and that has to do with the fact that these inflammatory agents are acting on this molecule to lower the threshold to heat and therefore, generate a perception of pain even in temperatures that normally you wouldn't consider painful. And understanding how that occurs and how changes in these molecule and how the structure of this molecule is involved in those sensitisation mechanisms is very important for understanding pain hypersensitivity, especially in the context of tissue injury. And looking at this structure of these special bat receptors gives us some clues about what parts of the molecule might be involved in those kinds of temperature shifts.
Chris - Who would've thought it?! We know that garlic drives vampires away but now, maybe the chilli attracts them. David, thank you very much. That's David Julius. He's from UCSF and you can find the work that he was talking about published this week, it's in the journal Nature.
16:21 - Making brains from skin
Making brains from skin
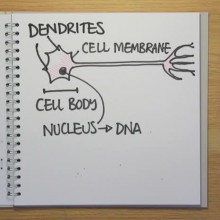
A way to turn skin cells directly into functioning brain cells has been announced by scientists in New York.
Asa Abeliovich, a researcher at Columbia University in New York, 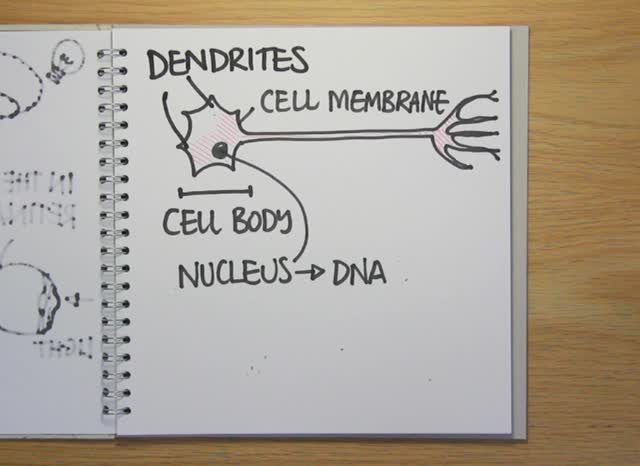 took human skin fibroblast cells and, using a disabled virus, added a handful of regulatory genes called Ascl1, Brn2 and Zic1. These normally act as forebrain transcriptional regulators, meaning that their role is to control the expression of other genes, but in this case they were also able to trigger up to 68% of the cells to begin to turn themselves into neurones.
took human skin fibroblast cells and, using a disabled virus, added a handful of regulatory genes called Ascl1, Brn2 and Zic1. These normally act as forebrain transcriptional regulators, meaning that their role is to control the expression of other genes, but in this case they were also able to trigger up to 68% of the cells to begin to turn themselves into neurones.
And just like normal nerve cells, the newly-produced neurones were capable of firing action potentials (electrical impulses) and their electrical activity could also be altered with nerve-selective drugs or chemicals. They also had thin axon-like processes capable of releasing nerve transmitter chemicals and, when injected into the developing nervous systems of mice, they survived and could even be found wired-up in the animals' brains after they were born.
In a formidable twist, skin cells from patients with Alzheimer's Disease were also transformed into brain cells that displayed the very same abnormal biochemical characteristics that typify the disease. "This is the first biological inroad for the modelling of sporadic illnesses," says Abeliovich.
Although this technique is not the first to turn skin cells into nerve cells, previous attempts to do this have involved first turning the cells into stem cells, called iPS cells, and then triggering them to re-specialise into neurones. But recent studies have shown that cells generated this way can be unreliable owing to mutations occuring in their DNA during the re-programming process. However, this new approach, described in the journal Cell, is one way around the problem.










Comments
Add a comment